SKIN
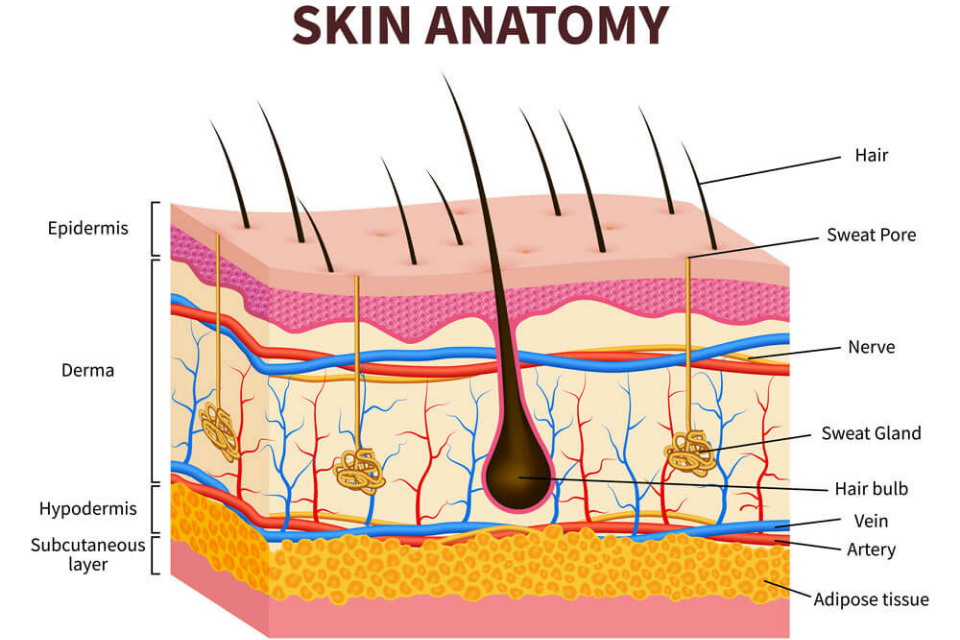
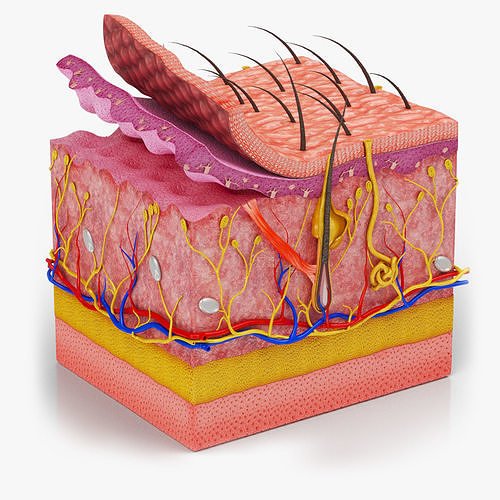
Skin is the largest organ of the integumentary system made up of multiple layers of epithelial tissues that guard underlying muscles and organs.
The adjective cutaneous literally means “of the skin” (from Latin cutis, skin).
As the interface with the surroundings, skin plays the most important role in protecting (the body) against pathogens. Its other main functions are insulation and temperature regulation, sensation, and synthesis of vitamin D and the protection of vitamin B folates.
Structure of skin:
Skin consists of
- An outer layer called epidermis.
- A middle layer called dermis.
- An inner layer called hypodermis.
Epidermis: It is made of stratified squamous epithelium and contains the following layers.
- Stratum cornium: Contains scale-like cells which are constantly replaced. These cells have a protein called keratin.
- Stratum lucidum: A glistening layer.
- Stratum granulosum: Has spindle-shaped cells with granules in the cytoplasm.
- Stratum germinativum: Contains cuboidal cells. The skin cells multiply in this layer.
Dermis: It is the inner layer which forms true skin. It contains the following structures:
- Melanocytes containing melanin pigment and some elastic fibers which maintain the texture of the skin.
- Arterial and venous capillaries and sensory nerve ending.
- Sweat and sebaceous glands.
- Hair roots and erector pill muscles (contraction of these muscles produce straightening of the hair)
Hypodermis: It is also called subcutaneous layer and is made up of specialized cells called lipocytes which store fat.
Secretions of skin:
Sweat: Sweat is secreted by sweat glands, which arise from dermis. They are twisted tubular glands and their ducts open in epidermis. Sweat glands are more numerous in the palms of hands and the sole of feet. Sweat contains mainly water, some salts and traces of other waste products.
Secretion of sebum: Sebum is a greasy secretion produced b sebaceous glands. They are small, flask-shaped glands present in dermis. They have a duct which opens into a hair follicle. The sebaceous glands are present in the skin of many parts except the palm of hands and sole of feet. Sebum keeps the skin oily and prevents it from drying.
PATHOLOGICAL CONDITIONS
Cutaneous lesions:
- Macule: The macule is the simplest dermatological lesion. It is flat and can only be seen and not felt. The macule is noted by a change in color of the skin. It may be brown, blue, red or exhibit a lesser pigment or an absence of pigment. The color of the lesion is one way in which a diagnosis may be focused.
- Papule: An inflammatory comedo that resembles a small, red bump on the skin.
- Nodule: A small solid collection of tissue, a nodule is palpable (can be felt). It may range in size from greater than 1.0 cm (3/8 inch) to somewhat less than 2 cm (13/16 inch) in diameter. A nodule may be present in the epidermis, dermis or subcutis (at any level in the skin).
The word “nodule” is the diminutive of “node” (a knot or knob) so a “nodule” means “a little knot or knob.”
- Plaque: Elevated flat-topped lesion>5mm
- Vesicle: Elevated fluid-filled lesions< 5mm.
- Bulla: Elevated fluid-filled lesion>5mm.
- Blister: Common term for vesicle of bulla.
- Pustule: Discrete, pus-filled raised area.
- Wheal: Pruritic, erythematous elevated area resulting from dermal edema.
- Scale: Dry, plate-like excrescence resulting from aberrant cornifications
- Lichenification: Thick, rough skin with prominent skin marking usually secondary to repeated rubbing.
- Excoriation: Linear, traumatic lesion resulting in epidermal breakage
- Onycholysis: Loss of nail substance.
ECZEMA
Eczema is a form of dermatitis, or inflammation of the upper layers of the skin.
The term eczema is broadly applied to a range of persistent skin conditions. These include dryness and recurring skin rashes which are characterized by one or more of these symptoms: redness, skin edema, itching and dryness, crusting, flaking, blistering, cracking, oozing, or bleeding. Areas of temporary skin discoloration may appear and are sometimes due to healed lesions, although scarring is rare
PSORIASIS
Psoriasis is a non-infectious, inflammatory disease of the skin characterized by itching, scaly red patches covered by scaly scales. The main abnormality in increased growth rate of basal layer of epidermis. Etiology is unknown, but there is a genetic predisposition. Many precipitating factors are known. Treatment includes keratolytics, steroids and PUVA (psoralen-ultraviolet A light therapy).
ACNE VULGARIS
This disorder affects many teenagers; obstruction at the exit of the pilosebaceous follicle obstructs the flow of sebum. Bacteria colonizes. In the skin break down the sebum producing inflammatory substances. Papules, pustules and cysts thus form. Treatment includes antibiotics and medications that dry skin.
DRUGS USED FOR DERMATOLOGICAL DISORDERS
- DEMULCENTS
- Glycyrrhiza
- Methylcellulose
- Propylene glycol
- Glycerine
- EMOLLIENTS
- Oliver oil, arachis oil, linseed oil, wool alcohol.
- Soft and hard paraffin, liquid paraffin
- ABSORBENTS AND PROTECTIVES
- Magnesium stearate, Zinc stearate.
- Talc, Calamine, Zinc oxide, Bentonite, starch, Boric acid.
- ASTRINGENTS
Tannic acid
Bismuth carbonate, Alum, Aluminium hydroxychloride/phenoslulfonate/Sulfate, Zinc oxide/ phenolsulfonate, Zirconyl hydroxychloride.
CAUSTIC AND ESCHAROTICS
Podophyllum resin
Silver nitrate
Phenol
Trichoroacetic acid Glacial acetic acid
KERATOLYTICS
Salicylic acid
Resorcinol
Benzoic acid
ANTI-SEBORRHEICS
Selenium sulfide
Zinc pyrithione
Corticosteroids
Nystatin
Sulfur, Resorcinol, Coaltar, Ammoniated mercury
Salicylic acid
MELANIZING AGENTS
Psoralen
Methoxsalen
DEMELANIZING AGENTS
Hydrquinone
Monobenzone
Azelaic acid
SUNSCREENS
Paraq-aminobenzoic acid (PABA)
Benzophenones
Cinnamates
DRUGS FOR ACNE VULGARIS
Benzoyl Peroxide
Retionic acid
Clindamycin
Erythromycin
Tetracyclines
ABBREVIATIONS
Bx : Biopsy
Derm : Dermatology
DLE : Discoid lupus erythematosus
PPD : Purified protein derivative
PUVA : Psoralen-ultraviolet. A light therapy
Subq : Subcutaneous
SLE : Systemic lupus erythematosus
HSV-I : HSV-I Herpes simplex virus type –I
HSV-I : Herpes simplex virus type –II